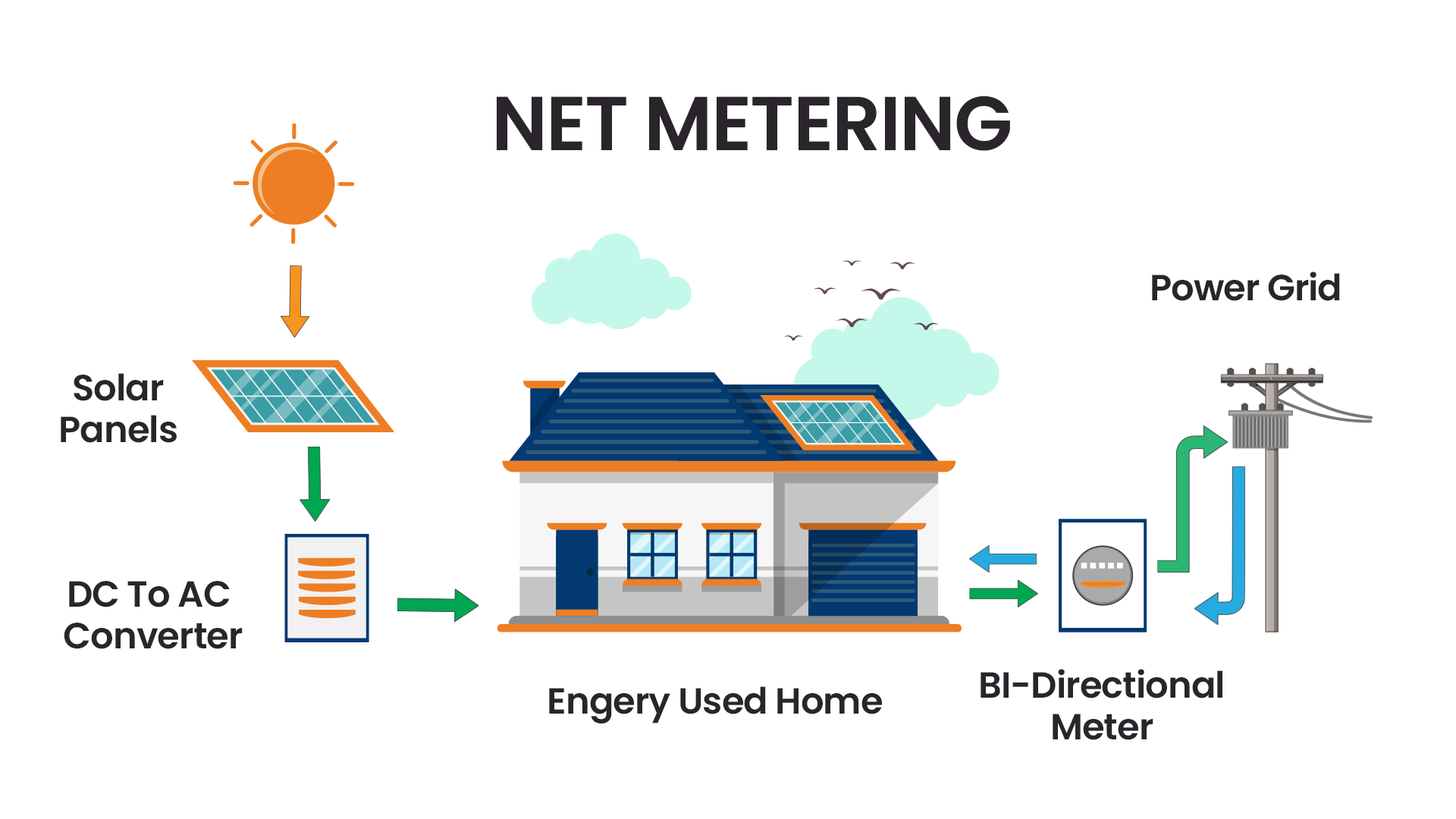
Net metering, within the Indian context, is a billing mechanism that enables consumers to offset their electricity bills by generating renewable energy and feeding excess power into the grid. Here’s a detailed overview tailored to the Indian jurisdiction:
1. Installation of Renewable Energy System: Homeowners or businesses install renewable energy systems, such as solar panels or wind turbines, on their premises to generate electricity from renewable sources.
2. Generation of Electricity: When these renewable energy systems produce electricity, they cater to the energy demands of the property first. Any surplus electricity beyond the immediate needs is then exported to the grid.
3. Bi-Directional Metering: To facilitate net metering, a bi-directional meter is installed by the utility company. This meter tracks the flow of electricity in two directions: from the grid to the consumer’s property when electricity is consumed, and from the consumer’s property to the grid when excess electricity is generated.
4. Credit Mechanism: Consumers receive credits on their electricity bills for the surplus electricity they export to the grid. These credits are typically calculated at the prevailing retail rate, equivalent to what the consumer would have paid to purchase the same amount of electricity from the utility company.
5. Offset Electricity Bills: The credits earned through net metering are utilized to offset the consumer’s electricity bills. If the consumer generates more electricity than they consume during a billing period, they can carry forward excess credits to future months or receive compensation for the surplus electricity, depending on the net metering regulations in place.
Net metering offers several advantages in the Indian context:
-Financial Savings: Consumers can significantly reduce their electricity bills by generating their own renewable energy and receiving credits for surplus generation.
-Environmental Benefits: Encouraging the adoption of renewable energy technologies helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and fosters environmental sustainability, which is particularly crucial in a country like India facing energy and environmental challenges.
-Energy Security: By promoting distributed generation from renewable sources, net metering contributes to enhancing energy security and reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
However, there are also challenges specific to the Indian context:
-Policy and Regulatory Framework: Net metering policies in India vary across states and may be subject to changes in regulations and tariffs, impacting the economics of renewable energy investments and the benefits accrued by consumers.
-Grid Integration Challenges: Integrating variable renewable energy sources into the grid poses technical challenges related to grid stability and management, requiring investments in grid infrastructure and smart grid technologies.
In conclusion, net metering plays a crucial role in promoting renewable energy adoption and achieving India’s energy and sustainability goals. However, its successful implementation requires a supportive policy and regulatory framework, along with investments in grid infrastructure and technology upgrades to ensure seamless integration of renewable energy into the electricity grid.