Understanding Open Access in the Energy Sector
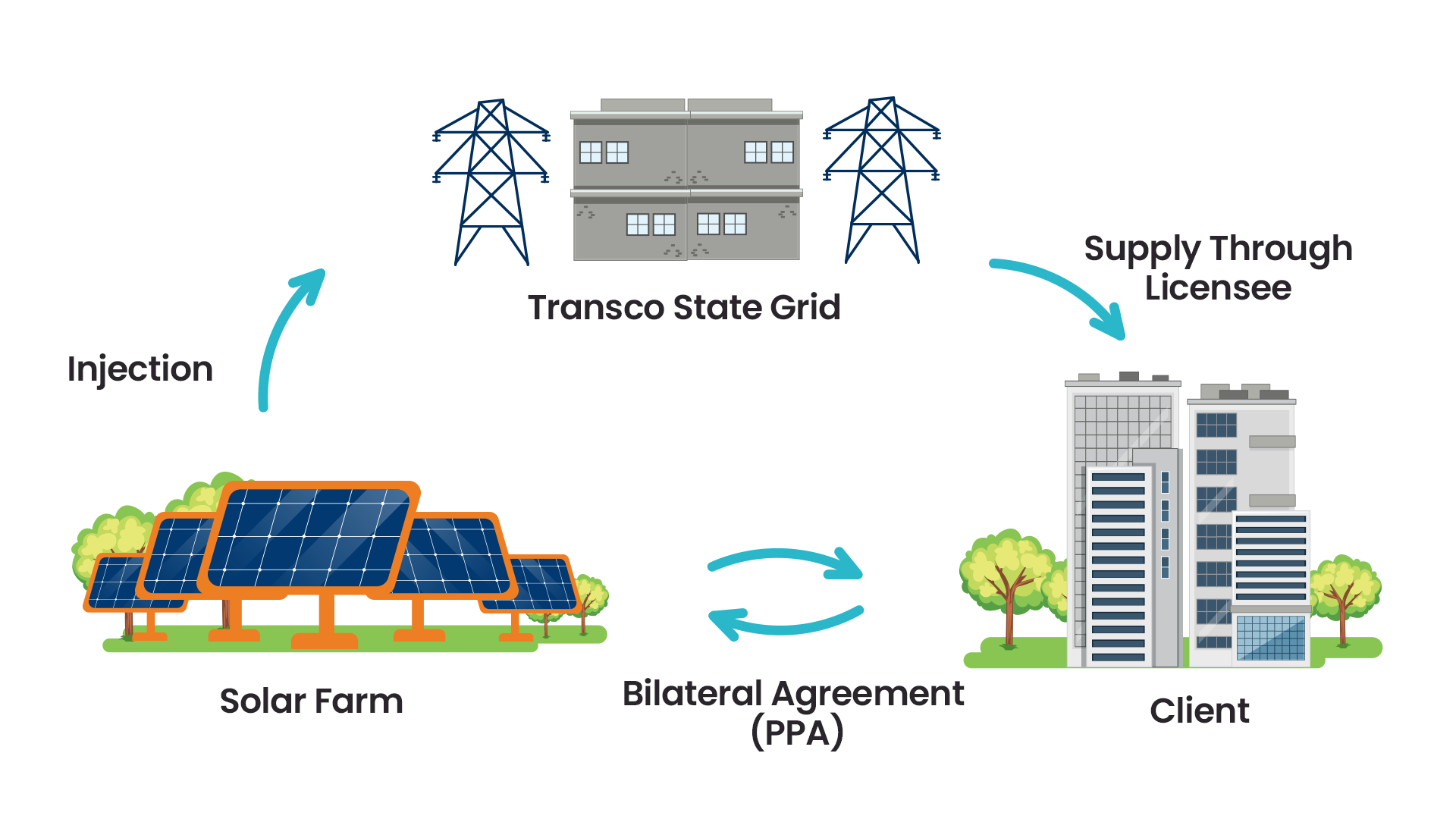
Open Access is a regulatory provision that allows consumers to procure electricity directly from generators or suppliers of their choice, bypassing the local distribution utility. This mechanism promotes competition in the electricity market by enabling consumers to access a wider range of suppliers and potentially lower electricity prices.
How Open Access Works:
- Regulatory Framework: Open Access is governed by regulations and policies set forth by regulatory bodies such as electricity regulatory commissions or energy regulatory authorities. These regulations define the terms and conditions under which consumers can access electricity from non-incumbent suppliers.
- Infrastructure: Open Access relies on a well-developed transmission and distribution infrastructure to facilitate the flow of electricity between generators, consumers, and the grid. Transmission lines and substations play a crucial role in transporting electricity from generators to consumers.
- Consumer Choice: Under Open Access, consumers have the freedom to choose their electricity supplier based on factors such as price, reliability, and sustainability. This empowers consumers to select suppliers that best meet their needs and preferences, driving competition in the market.
- Billing and Settlement: The billing and settlement process under Open Access involves coordination between various stakeholders, including generators, suppliers, distribution utilities, and consumers. Bills are typically generated based on the amount of electricity consumed and the agreed-upon tariffs or rates.
Benefits of Open Access:
- Competitive Pricing: Open Access encourages competition among suppliers, leading to competitive pricing and potentially lower electricity costs for consumers.
- Energy Diversification: By allowing consumers to choose their electricity supplier, Open Access promotes energy diversification by enabling access to a variety of generation sources, including renewable energy.
- Efficiency and Innovation: Increased competition in the electricity market encourages suppliers to improve efficiency and innovate to attract and retain customers, leading to overall improvements in service quality and reliability.
- Empowerment of Consumers: Open Access gives consumers greater control over their energy choices, empowering them to make informed decisions based on their preferences and values.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Infrastructure Constraints: In some regions, limited transmission and distribution infrastructure may pose challenges to the implementation of Open Access, limiting the ability of consumers to access electricity from alternative suppliers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory requirements and administrative procedures can be complex and time-consuming for both consumers and suppliers seeking to participate in Open Access programs.
- Market Dynamics: The effectiveness of Open Access may be influenced by market dynamics, including supply and demand conditions, regulatory stability, and the presence of incumbent utilities.
- Risk Management: Consumers and suppliers participating in Open Access programs may be exposed to risks such as price volatility, regulatory changes, and operational disruptions, necessitating effective risk management strategies.
In summary, Open Access plays a critical role in promoting competition, innovation, and consumer choice in the electricity market. By enabling consumers to access electricity from a variety of suppliers, Open Access contributes to a more efficient, diverse, and resilient energy ecosystem. However, addressing challenges related to infrastructure, regulation, and risk management is essential to realizing the full potential of Open Access and maximizing its benefits for all stakeholders involved.